Abstract
Background: Event-free survival at 24 months (EFS24) is an important clinical endpoint in newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma, and patients who achieve EFS24 with frontline immunochemotherapy have minimal loss of lifetime compared to age- and sex-matched general population. However, the prognostic role of EFS24 in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) has not been well studied, possibly due to the perception of continued relapse pattern and poor survival outcome of MCL historically. A recent study from our group demonstrated evolving frontline therapy pattern from 2002-2009 ("Era 1") to 2010-2015 ("Era 2") which was associated with improved EFS and overall survival (OS) in Era 2. In the current study, we sought to explore the prognostic role of EFS24 in the two eras.
Methods: Patients with newly diagnosed MCL from 9/2002 through 6/2015 were identified from Molecular Epidemiology Resource (MER), a prospective cohort study of the University of Iowa/Mayo Clinic Lymphoma SPORE. OS was defined as time from diagnosis (or the EFS24 defining event where applicable) to death from any cause and was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Expected OS accounting for age and sex was generated in R by using the general US population as the reference group. Observed versus expected OS was summarized by using standardized mortality ratio (SMR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) of observed to expected deaths. Cumulative incidence of lymphoma-specific death was analyzed using Gray's test, with deaths from all other causes treated as competing events.
Results: A total of 343 patients were included, 175 from Era 1 (median follow-up 13.0 years) and 168 from Era 2 (median follow-up 6.9 years). Age, sex and simplified MIPI score were similar between the 2 groups. Patients diagnosed in Era 2 had better OS, with a 5-year OS of 68.4% vs 59.2% (simplified MIPI-adjusted hazard ratio 0.68, 95% CI 0.50-0.93).
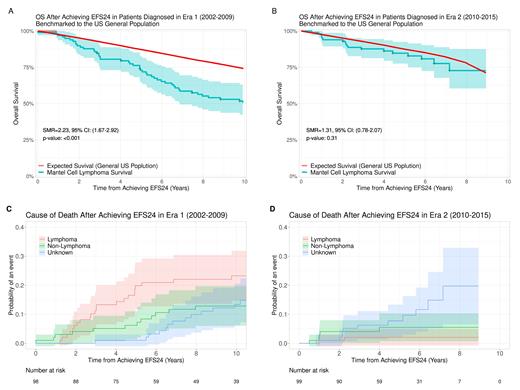
Patients diagnosed in both eras had inferior OS compared to the general population, with an SMR of 3.26 (95% CI 2.70-3.89, P<0.001) in Era 1 and 2.63 (95% CI 2.03-3.36, P<0.001) in Era 2. Patients diagnosed in Era 1 who achieved EFS24 (n=98) still had inferior OS compared to the general population, with an SMR of 2.23 (95% CI 1.67-2.92, P<0.001) (Figure 1A). In contrast, for patients diagnosed in Era 2 who achieved EFS24 (n=99), no evidence of OS difference was found compared to the general population, with an SMR of 1.31 (95% CI 0.78-2.07, P=0.31) (Figure 1B).
The primary cause of death after diagnosis was lymphoma-related for patients diagnosed in both eras. The 5-year rate of lymphoma-related death was 28.8% in Era 1 and 20.5% in Era 2. In patients who were diagnosed in Era 1 and achieved EFS24, the primary cause of death after achieving EFS24 remained to be lymphoma-related, with a 5-year rate of 19.8% compared to 6.2% for lymphoma-unrelated causes (Figure 1C). In contrast, in patients who were diagnosed in Era 2 and achieved EFS24, the rate of lymphoma-related death was no longer higher than that of lymphoma-unrelated death, with a 5-year rate of 2.1% vs 5.5%, respectively (Figure 1D).
In a sensitivity analysis restricted to only patients who received standard frontline immunochemotherapy, similar results were obtained. For example, in patients who achieved EFS24, the SMR compared to the general population was 2.89 (95% CI 2.00-4.04, P<0.001) in Era 1 and 0.89 (95% CI 0.43-1.64, P=0.82) in Era 2. The 5-year rates of deaths due to lymphoma-related vs lymphoma-unrelated causes were 20.7% vs 6.2% in Era 1 and 1.3% vs 4.9% in Era 2.
Conclusions: MCL survival outcome has improved for patients first diagnosed in the more recent era (2010-2015, compared to 2002-2009), likely due to improved frontline therapy as well as better salvage treatments (such as lenalidomide and BTK inhibitors). In the more recent treatment era, patients who achieved EFS24 had survival approaching the age- and sex-matched general population. In addition, these patients had a low risk of dying from lymphoma and were more likely to die from other causes. Longer follow-up (e.g., in Era 2) and external validation in other series are necessary to confirm the prognostic role of EFS24. With more efficacious salvage treatment options and likely continued improvement of OS in MCL, EFS24 may become an important clinical endpoint in frontline therapy of MCL.
Wang: TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eli Lilly: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Research Funding; InnoCare: Research Funding; LOXO Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding. Maurer: Morphosys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Research Funding; Nanostring: Research Funding. Link: Novartis, Jannsen: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; MEI: Consultancy. Farooq: Kite, a Gilead Company: Honoraria. Paludo: Karyopharm: Research Funding. Witzig: Celgene/BMS, Acerta Pharma, Kura Oncology, Acrotech Biopharma, Karyopharm Therapeutics: Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutics, Celgene/BMS, Incyte, Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Habermann: Seagen: Other: Data Monitoring Committee; Tess Therapeutics: Other: Data Monitoring Committee; Incyte: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Morphosys: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Loxo Oncology: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Eli Lilly & Co.,: Other: Scientific Advisor. Cerhan: Regeneron Genetics Center: Other: Research Collaboration; Celgene/BMS: Other: Connect Lymphoma Scientific Steering Committee, Research Funding; NanoString: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Nowakowski: Celgene, NanoString Technologies, MorphoSys: Research Funding; Celgene, MorphoSys, Genentech, Selvita, Debiopharm Group, Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal